The priority of today’s workforce is no longer limited to employment itself, but extends to quality of life at the workplace.
This reality is pushing industrial parks to transform toward more sustainable models, where healthcare and education become benchmarks for long-term workforce commitment.
The following article from KTG Industrial discusses the impact of social welfare infrastructure on the labor community in today’s industrial sector.
Why do education and healthcare determine workforce retention?
Education and healthcare infrastructure today go beyond their role as social welfare services; they have become integral to the ESG-focused developer strategies.
When essential needs are adequately met, workers tend to feel more secure in a sustainable manufacturing environment. Specifically, these factors deliver three clear impacts:
Stabilizing workers’ living conditions and mental well-being
Accessible school systems and healthcare facilities help reduce daily life pressures, especially for migrant workers and lower-income groups.
When children’s education and healthcare needs are ensured, workers maintain greater peace of mind and stability throughout their employment.

Convenient education and healthcare help workers feel secure and remain stable over the long term
Building long-term attachment to enterprises and local communities
Adequate education and healthcare help form strong and lasting connections between workers, enterprises, and the areas in which they live.
This enables workers to view industrial parks not merely as temporary workplaces, but as places where they can settle and build long-term lives.
Reducing turnover and improving productivity
When living conditions improve, employee turnover and labor mobility decline significantly.
Workforce stability allows enterprises to maintain production continuity while enhancing productivity and operational efficiency over the long term.
Education infrastructure: Retaining workers from the foundation
Education is considered a fundamental factor that enables workers to feel secure and commit long term to industrial parks.
When children’s education and opportunities for skills development are available near where people live and work, workers are more likely to stay rather than leave.
Schools near industrial parks: A settlement solution for workers
School systems and childcare facilities located close to industrial parks help workers stabilize family life.
As a result, long-distance commuting or sending children back to their hometowns is reduced, mental pressure is eased, and long-term attachment increases.
Vocational training and Industry 4.0
Skills training programs implemented directly within industrial parks support workers in accessing new technologies.
When skills are enhanced and career pathways are clearly defined, attachment to enterprises becomes more sustainable.
Investment in education and workforce retention effectiveness
In practice, investment in education is closely linked to industrial performance.
Industrial parks that prioritize education typically record higher employee retention rates while also improving productivity and workforce stability.

Investment in education helps industrial parks retain workers and enhance productivity
Healthcare infrastructure: Protecting health and maintaining production continuity
Alongside education, healthcare has a direct impact on workers’ physical condition and the continuity of production activities.
An appropriate healthcare system helps enterprises reduce operational disruptions and improve the quality of human resources.
On-site clinics and regional hospitals
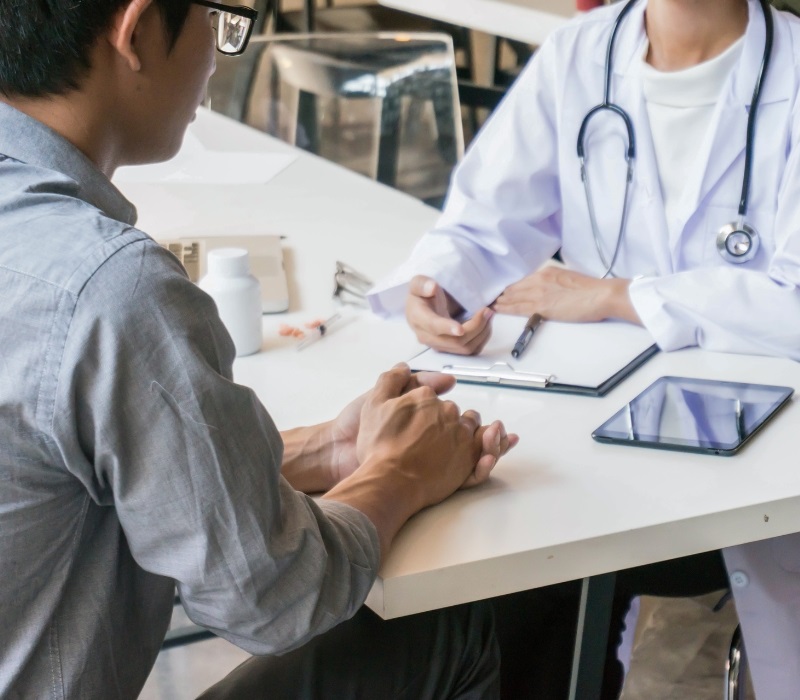
The provision of clinics within industrial parks or linkages with regional hospitals enables timely healthcare for workers.
As a result, sick leave duration is reduced, while preventive healthcare activities can be implemented more effectively.

Clinics and hospitals near industrial parks help reduce sick leave and stabilize production
Integrated healthcare (Workplace Healthcare)
Integrated workplace healthcare models support regular health monitoring and timely handling of emerging issues.
This not only helps minimize machine downtime but also ensures long-term health and energy recovery for workers.
Practical evidence
In practice, investment in healthcare services and incentives in production areas can increase workforce retention rates by approximately 35 to 50%, particularly in labor-intensive industries.
Overall impact and strategic value
Effective social welfare reduces job hopping
When essential needs related to housing, education, and healthcare are addressed in a coordinated manner, workers are more likely to remain with their employers over the long term.
As a result, job hopping and labor turnover driven by living cost pressures decline significantly.
Competitive advantage of industrial parks
In Vietnam, investment in social infrastructure is becoming an important competitive advantage for industrial parks.
This approach not only enhances productivity but also safeguards workers’ rights, aligning with the increasingly stringent requirements of global supply chains.
Conclusion
In summary, investment in education and healthcare infrastructure not only improves worker welfare but also establishes a stable foundation for the long-term development of industrial parks.
When social welfare needs are adequately met, enterprises can stabilize their workforce, improve production efficiency, and strengthen competitiveness in attracting and retaining labor.